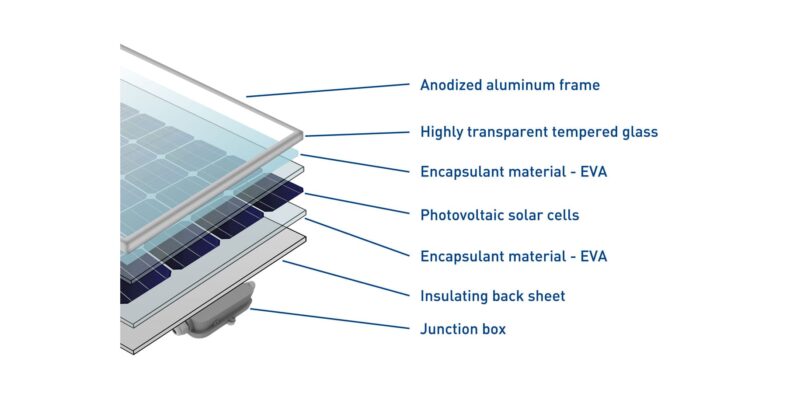
In the ever-evolving quest for sustainable energy solutions, innovation often arises from the most unexpected places. Enter solar carports, a creative blend of functionality and eco-friendliness that has been quietly revolutionizing the way we think about energy generation and space utilization.
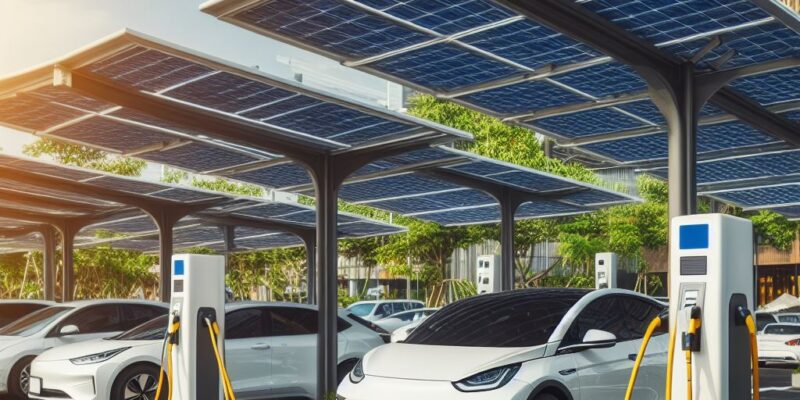
Imagine a vast parking lot, its expanse typically reserved for vehicles to rest under the sun. Now, picture this same space not only sheltering cars but also capturing sunlight to generate clean, renewable energy. This is precisely what solar carports offer: a dual-purpose solution that maximizes the utility of available space.
Parking lots are ubiquitous features of urban and suburban landscapes, often sprawling across vast areas with minimal vertical structures. Traditionally, these spaces serve a singular function – providing a place for vehicles to park. However, the introduction of solar carports transforms these asphalt expanses into energy-generating powerhouses.
By installing solar panels atop sturdy support structures, carports harness the sun’s energy while still fulfilling their primary role of providing shade and protection for parked vehicles. This repurposing of space not only reduces the environmental footprint of parking facilities but also contributes to the renewable energy grid, offsetting traditional energy sources and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Advantages of Solar Carports
- Space Optimization:
Solar carports make efficient use of space that would otherwise remain underutilized.
They are particularly beneficial in areas where land availability is limited, such as densely populated urban areas or campuses with expansive parking lots.
- Clean Energy Generation:
By harnessing solar power, carports contribute to the generation of clean, renewable energy, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating environmental impact.
This aligns with sustainability goals and helps organizations and communities meet renewable energy targets.
- Cost Savings:
While the initial investment may be higher than traditional parking structures, solar carports offer long-term cost savings through reduced energy bills and potential revenue generation from excess energy production.
They also provide protection for vehicles, reducing maintenance costs associated with exposure to the elements.
In the journey towards a sustainable future, innovation plays a pivotal role in reshaping our infrastructure and habits. Solar carports exemplify this ethos, offering a practical solution to the dual challenges of space optimization and clean energy generation.
As we continue to embrace renewable energy technologies, the widespread adoption of solar carports holds the promise of not only reducing our environmental impact but also transforming mundane spaces into engines of sustainability. By harnessing the power of the sun, we are driving towards a brighter, cleaner, and more sustainable future, one parking space at a time.