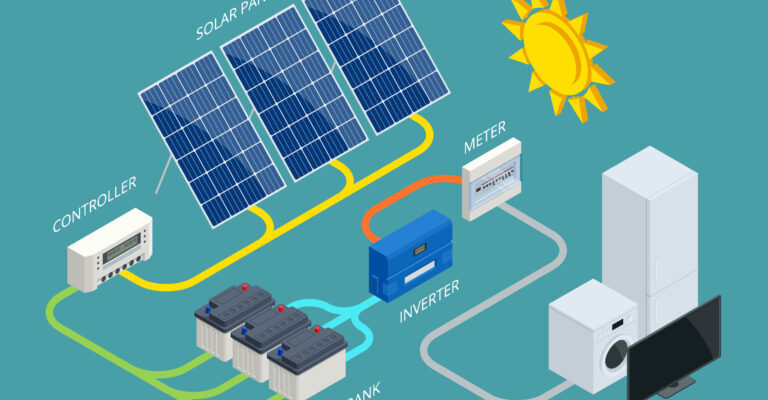
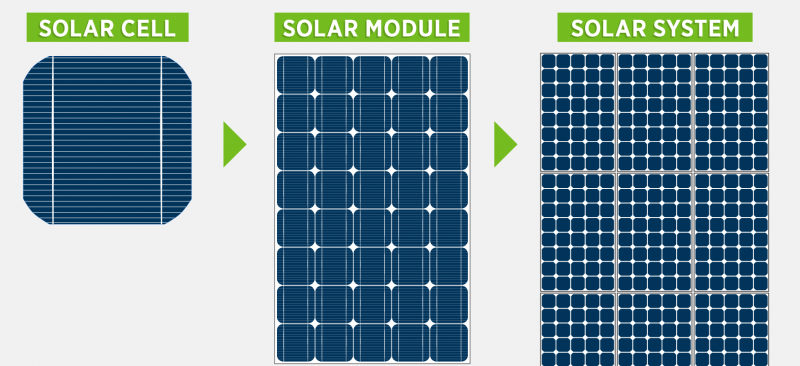
As Earth Day is behind us, it’s crucial to reflect on the steps we’re taking to preserve our planet and mitigate the effects of climate change. One of the most promising solutions in our arsenal is solar energy. Solar power has emerged as a beacon of hope, offering a clean, renewable alternative to fossil fuels.
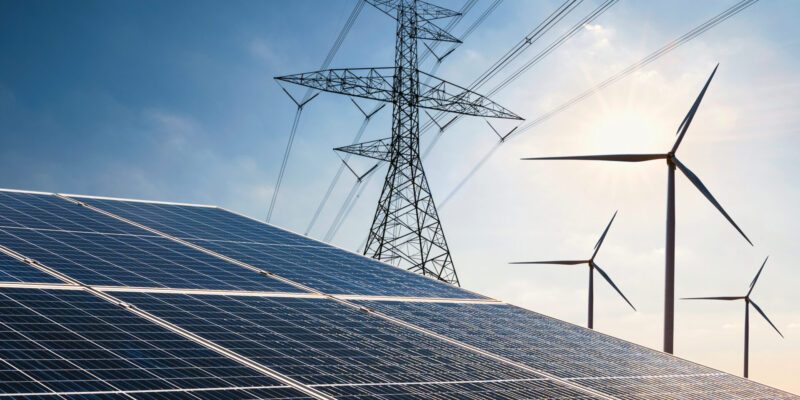
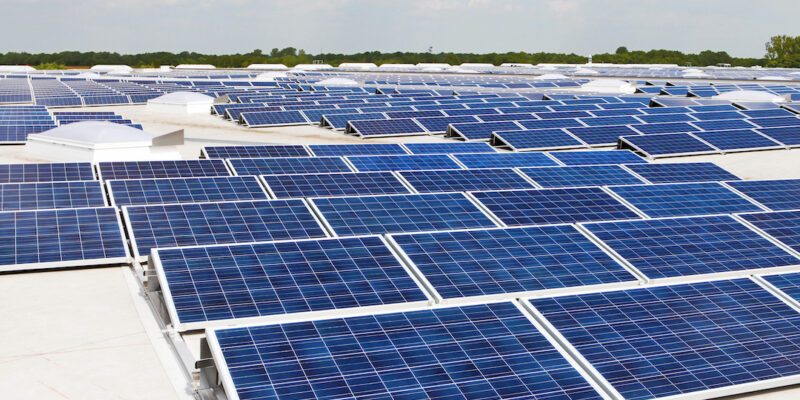
In recent years, solar energy has experienced a remarkable surge in popularity and accessibility. Advances in technology, coupled with decreasing costs, have made solar power more affordable and efficient than ever before. From rooftop solar panels to large-scale solar farms, this renewable energy source is revolutionizing the way we power our world.
One of the most significant benefits of solar energy is its ability to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike fossil fuels such as coal and natural gas, solar power generates electricity without emitting harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. By harnessing the energy of the sun, we can significantly decrease our reliance on carbon-intensive energy sources and combat climate change.
In addition to curbing carbon emissions, solar energy helps preserve our precious natural resources. Unlike finite fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, the sun provides an abundant and inexhaustible source of energy. By harnessing solar power, we can reduce our dependence on finite resources, protecting delicate ecosystems and biodiversity in the process.
The transition to solar energy is not only beneficial for the environment but also for the economy. The solar industry has become a major source of employment, providing jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance. As demand for solar energy continues to grow, so too will the need for skilled workers, driving economic growth and opportunity.
As we celebrated Earth Day, we recognized the transformative power of solar energy in our quest to save the planet. By harnessing the boundless energy of the sun, we can reduce carbon emissions, preserve natural resources, and create green jobs. However, our journey towards a sustainable future is far from over. It’s imperative that we continue to advocate for policies that support renewable energy and invest in innovative technologies that will drive us towards a cleaner, greener tomorrow. Together, we can harness the power of the sun to safeguard our Earth for generations to come.