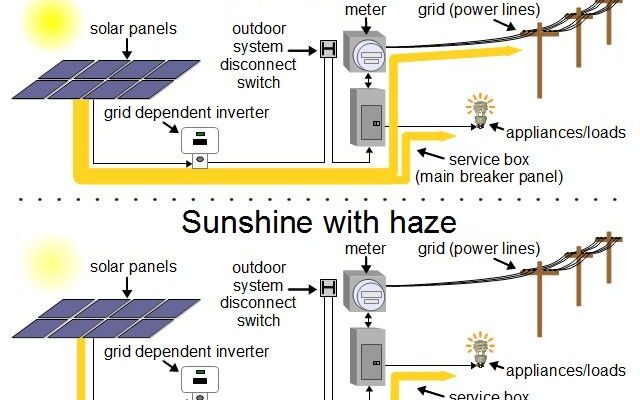
Solar power has gained popularity as a clean, renewable energy source over the past few decades.
However, along with its growing acceptance, several myths and misconceptions have emerged,
hindering the widespread adoption of this eco-friendly technology. This article aims to debunk
some of the most common solar power myths and shed light on the truth behind them.
Myth 1: Solar panels are only effective in sunny regions.
Reality: While it's true that solar panels generate more electricity in direct sunlight, they can still
produce energy on cloudy days or in regions with less sunshine. Modern solar technology has improved
significantly, making it viable in various climates, including overcast or cold weather places. Solar
panels generate electricity, albeit at a slightly reduced efficiency, even during cloudy days.
Myth 2: Solar panels are too expensive and not cost-effective.
Reality: The cost of solar panels has drastically decreased, making them more affordable
than ever. Additionally, various financial incentives and government subsidies, such as tax credits and
rebates, are available to encourage homeowners and businesses to invest in solar energy. Although the
upfront cost may seem significant, the long-term savings on electricity bills often outweigh the initial
investment, making solar power a cost-effective choice in the long run.
Myth 3: Solar panels require constant maintenance.
Reality: Solar panels are designed to be durable and low-maintenance. They have no moving parts,
reducing the risk of mechanical failures. Routine cleaning to remove dirt and debris is generally
sufficient to maintain efficiency. Most reputable solar panel manufacturers offer warranties and
maintenance plans, further ensuring the longevity and performance of the panels.
Myth 4: Solar energy is not reliable, and storage is impractical.
Reality: While solar energy is intermittent, advancements in energy storage technologies, such as
batteries, have made it possible to store excess energy for later use. With efficient energy storage
solutions, solar power can provide a reliable energy source, even during grid outages or at night.
Myth 5: Solar energy is only suitable for residential use.
Reality: Solar power is not limited to residential applications. Many commercial and industrial
establishments are increasingly adopting solar energy to meet their power needs and reduce
operational costs. Moreover, large-scale solar farms are becoming common, contributing significantly to
the overall renewable energy mix.
In conclusion, dispelling these common solar power myths is crucial for fostering greater acceptance and
adoption of solar energy. As technology advances, solar power will play a pivotal role in
shaping our planet’s more sustainable and cleaner future. Understanding the reality of solar energy
is essential for making informed decisions about embracing this renewable energy source.